Control System Plots
This module contains plotting functions for some of the common plots used in control system. Matplotlib will be required as an external dependency if the user wants the plots. To get only the numerical data of the plots, NumPy will be required as external dependency.
Pole-Zero Plot
- control_plots.pole_zero_plot(pole_color='blue', pole_markersize=10, zero_color='orange', zero_markersize=7, grid=True, show_axes=True, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the Pole-Zero plot (also known as PZ Plot or PZ Map) of a system.
A Pole-Zero plot is a graphical representation of a system’s poles and zeros. It is plotted on a complex plane, with circular markers representing the system’s zeros and ‘x’ shaped markers representing the system’s poles.
- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant type systems
The system for which the pole-zero plot is to be computed.
pole_color : str, tuple, optional
The color of the pole points on the plot. Default color is blue. The color can be provided as a matplotlib color string, or a 3-tuple of floats each in the 0-1 range.
pole_markersize : Number, optional
The size of the markers used to mark the poles in the plot. Default pole markersize is 10.
zero_color : str, tuple, optional
The color of the zero points on the plot. Default color is orange. The color can be provided as a matplotlib color string, or a 3-tuple of floats each in the 0-1 range.
zero_markersize : Number, optional
The size of the markers used to mark the zeros in the plot. Default zero markersize is 7.
grid : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will have a grid. Defaults to True.show_axes : boolean, optional
If
True, the coordinate axes will be shown. Defaults to False.show : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will be displayed otherwise the equivalent matplotlibplotobject will be returned. Defaults to True.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import pole_zero_plot >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s**2 + 1, s**4 + 4*s**3 + 6*s**2 + 5*s + 2, s) >>> pole_zero_plot(tf1)
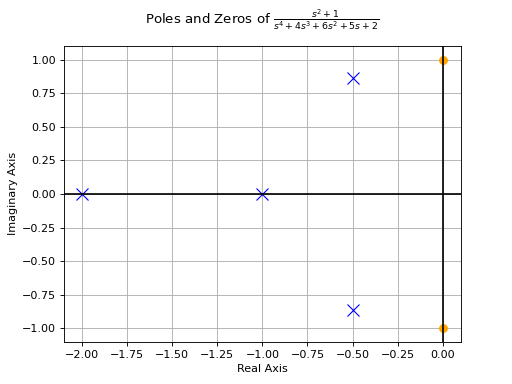
See also
References
- control_plots.pole_zero_numerical_data()[source]
Returns the numerical data of poles and zeros of the system. It is internally used by
pole_zero_plotto get the data for plotting poles and zeros. Users can use this data to further analyse the dynamics of the system or plot using a different backend/plotting-module.- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant
The system for which the pole-zero data is to be computed.
- Returns
tuple : (zeros, poles)
zeros = Zeros of the system. NumPy array of complex numbers. poles = Poles of the system. NumPy array of complex numbers.
- Raises
NotImplementedError
When a SISO LTI system is not passed.
When time delay terms are present in the system.
ValueError
When more than one free symbol is present in the system. The only variable in the transfer function should be the variable of the Laplace transform.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import pole_zero_numerical_data >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s**2 + 1, s**4 + 4*s**3 + 6*s**2 + 5*s + 2, s) >>> pole_zero_numerical_data(tf1) ([-0.+1.j 0.-1.j], [-2. +0.j -0.5+0.8660254j -0.5-0.8660254j -1. +0.j ])
See also
Bode Plot
- control_plots.bode_plot(initial_exp=- 5, final_exp=5, grid=True, show_axes=False, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the Bode phase and magnitude plots of a continuous-time system.
- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant type
The LTI SISO system for which the Bode Plot is to be computed.
initial_exp : Number, optional
The initial exponent of 10 of the semilog plot. Defaults to -5.
final_exp : Number, optional
The final exponent of 10 of the semilog plot. Defaults to 5.
show : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will be displayed otherwise the equivalent matplotlibplotobject will be returned. Defaults to True.prec : int, optional
The decimal point precision for the point coordinate values. Defaults to 8.
grid : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will have a grid. Defaults to True.show_axes : boolean, optional
If
True, the coordinate axes will be shown. Defaults to False.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import bode_plot >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(1*s**2 + 0.1*s + 7.5, 1*s**4 + 0.12*s**3 + 9*s**2, s) >>> bode_plot(tf1, initial_exp=0.2, final_exp=0.7)
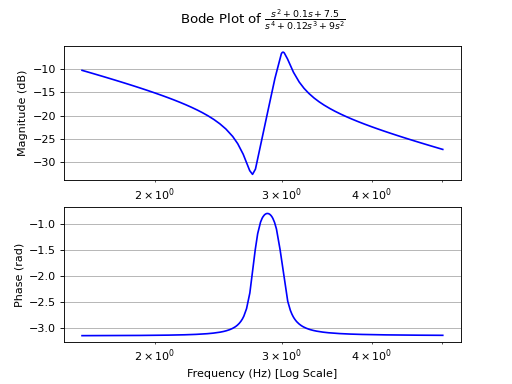
See also
- control_plots.bode_magnitude_plot(initial_exp=- 5, final_exp=5, color='b', show_axes=False, grid=True, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the Bode magnitude plot of a continuous-time system.
See
bode_plotfor all the parameters.
- control_plots.bode_phase_plot(initial_exp=- 5, final_exp=5, color='b', show_axes=False, grid=True, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the Bode phase plot of a continuous-time system.
See
bode_plotfor all the parameters.
- control_plots.bode_magnitude_numerical_data(initial_exp=- 5, final_exp=5, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the numerical data of the Bode magnitude plot of the system. It is internally used by
bode_magnitude_plotto get the data for plotting Bode magnitude plot. Users can use this data to further analyse the dynamics of the system or plot using a different backend/plotting-module.- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant
The system for which the data is to be computed.
initial_exp : Number, optional
The initial exponent of 10 of the semilog plot. Defaults to -5.
final_exp : Number, optional
The final exponent of 10 of the semilog plot. Defaults to 5.
- Returns
tuple : (x, y)
x = x-axis values of the Bode magnitude plot. y = y-axis values of the Bode magnitude plot.
- Raises
NotImplementedError
When a SISO LTI system is not passed.
When time delay terms are present in the system.
ValueError
When more than one free symbol is present in the system. The only variable in the transfer function should be the variable of the Laplace transform.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import bode_magnitude_numerical_data >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s**2 + 1, s**4 + 4*s**3 + 6*s**2 + 5*s + 2, s) >>> bode_magnitude_numerical_data(tf1) ([1e-05, 1.5148378120533502e-05,..., 68437.36188804005, 100000.0], [-6.020599914256786, -6.0205999155219505,..., -193.4117304087953, -200.00000000260573])
See also
- control_plots.bode_phase_numerical_data(initial_exp=- 5, final_exp=5, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the numerical data of the Bode phase plot of the system. It is internally used by
bode_phase_plotto get the data for plotting Bode phase plot. Users can use this data to further analyse the dynamics of the system or plot using a different backend/plotting-module.- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant
The system for which the Bode phase plot data is to be computed.
initial_exp : Number, optional
The initial exponent of 10 of the semilog plot. Defaults to -5.
final_exp : Number, optional
The final exponent of 10 of the semilog plot. Defaults to 5.
- Returns
tuple : (x, y)
x = x-axis values of the Bode phase plot. y = y-axis values of the Bode phase plot.
- Raises
NotImplementedError
When a SISO LTI system is not passed.
When time delay terms are present in the system.
ValueError
When more than one free symbol is present in the system. The only variable in the transfer function should be the variable of the Laplace transform.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import bode_phase_numerical_data >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s**2 + 1, s**4 + 4*s**3 + 6*s**2 + 5*s + 2, s) >>> bode_phase_numerical_data(tf1) ([1e-05, 1.4472354033813751e-05, 2.035581932165858e-05,..., 47577.3248186011, 67884.09326036123, 100000.0], [-2.5000000000291665e-05, -3.6180885085e-05, -5.08895483066e-05,...,-3.1415085799262523, -3.14155265358979])
See also
Impulse-Response Plot
- control_plots.impulse_response_plot(color='b', prec=8, lower_limit=0, upper_limit=10, show_axes=False, grid=True, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the unit impulse response (Input is the Dirac-Delta Function) of a continuous-time system.
- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant type
The LTI SISO system for which the Impulse Response is to be computed.
color : str, tuple, optional
The color of the line. Default is Blue.
show : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will be displayed otherwise the equivalent matplotlibplotobject will be returned. Defaults to True.lower_limit : Number, optional
The lower limit of the plot range. Defaults to 0.
upper_limit : Number, optional
The upper limit of the plot range. Defaults to 10.
prec : int, optional
The decimal point precision for the point coordinate values. Defaults to 8.
show_axes : boolean, optional
If
True, the coordinate axes will be shown. Defaults to False.grid : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will have a grid. Defaults to True.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import impulse_response_plot >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(8*s**2 + 18*s + 32, s**3 + 6*s**2 + 14*s + 24, s) >>> impulse_response_plot(tf1)
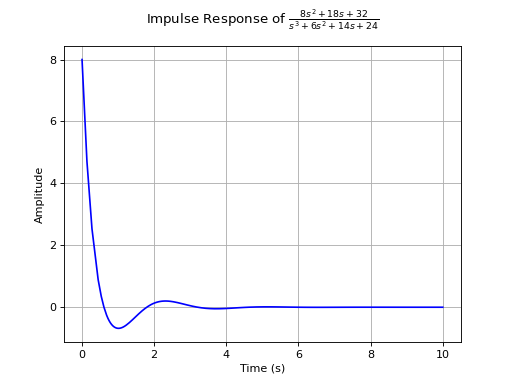
See also
References
- control_plots.impulse_response_numerical_data(prec=8, lower_limit=0, upper_limit=10, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the numerical values of the points in the impulse response plot of a SISO continuous-time system. By default, adaptive sampling is used. If the user wants to instead get an uniformly sampled response, then
adaptivekwarg should be passedFalseandnb_of_pointsmust be passed as additional kwargs. Refer to the parameters of classsympy.plotting.plot.LineOver1DRangeSeriesfor more details.- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant
The system for which the impulse response data is to be computed.
prec : int, optional
The decimal point precision for the point coordinate values. Defaults to 8.
lower_limit : Number, optional
The lower limit of the plot range. Defaults to 0.
upper_limit : Number, optional
The upper limit of the plot range. Defaults to 10.
kwargs :
Additional keyword arguments are passed to the underlying
sympy.plotting.plot.LineOver1DRangeSeriesclass.- Returns
tuple : (x, y)
x = Time-axis values of the points in the impulse response. NumPy array. y = Amplitude-axis values of the points in the impulse response. NumPy array.
- Raises
NotImplementedError
When a SISO LTI system is not passed.
When time delay terms are present in the system.
ValueError
When more than one free symbol is present in the system. The only variable in the transfer function should be the variable of the Laplace transform.
When
lower_limitparameter is less than 0.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import impulse_response_numerical_data >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s, s**2 + 5*s + 8, s) >>> impulse_response_numerical_data(tf1) ([0.0, 0.06616480200395854,... , 9.854500743565858, 10.0], [0.9999999799999999, 0.7042848373025861,...,7.170748906965121e-13, -5.1901263495547205e-12])
See also
Step-Response Plot
- control_plots.step_response_plot(color='b', prec=8, lower_limit=0, upper_limit=10, show_axes=False, grid=True, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the unit step response of a continuous-time system. It is the response of the system when the input signal is a step function.
- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant type
The LTI SISO system for which the Step Response is to be computed.
color : str, tuple, optional
The color of the line. Default is Blue.
show : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will be displayed otherwise the equivalent matplotlibplotobject will be returned. Defaults to True.lower_limit : Number, optional
The lower limit of the plot range. Defaults to 0.
upper_limit : Number, optional
The upper limit of the plot range. Defaults to 10.
prec : int, optional
The decimal point precision for the point coordinate values. Defaults to 8.
show_axes : boolean, optional
If
True, the coordinate axes will be shown. Defaults to False.grid : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will have a grid. Defaults to True.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import step_response_plot >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(8*s**2 + 18*s + 32, s**3 + 6*s**2 + 14*s + 24, s) >>> step_response_plot(tf1)
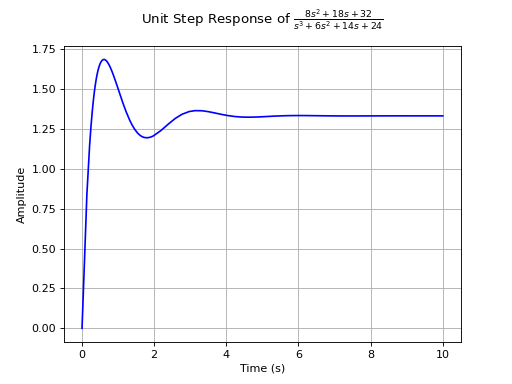
See also
References
- control_plots.step_response_numerical_data(prec=8, lower_limit=0, upper_limit=10, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the numerical values of the points in the step response plot of a SISO continuous-time system. By default, adaptive sampling is used. If the user wants to instead get an uniformly sampled response, then
adaptivekwarg should be passedFalseandnb_of_pointsmust be passed as additional kwargs. Refer to the parameters of classsympy.plotting.plot.LineOver1DRangeSeriesfor more details.- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant
The system for which the unit step response data is to be computed.
prec : int, optional
The decimal point precision for the point coordinate values. Defaults to 8.
lower_limit : Number, optional
The lower limit of the plot range. Defaults to 0.
upper_limit : Number, optional
The upper limit of the plot range. Defaults to 10.
kwargs :
Additional keyword arguments are passed to the underlying
sympy.plotting.plot.LineOver1DRangeSeriesclass.- Returns
tuple : (x, y)
x = Time-axis values of the points in the step response. NumPy array. y = Amplitude-axis values of the points in the step response. NumPy array.
- Raises
NotImplementedError
When a SISO LTI system is not passed.
When time delay terms are present in the system.
ValueError
When more than one free symbol is present in the system. The only variable in the transfer function should be the variable of the Laplace transform.
When
lower_limitparameter is less than 0.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import step_response_numerical_data >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s, s**2 + 5*s + 8, s) >>> step_response_numerical_data(tf1) ([0.0, 0.025413462339411542, 0.0484508722725343, ... , 9.670250533855183, 9.844291913708725, 10.0], [0.0, 0.023844582399907256, 0.042894276802320226, ..., 6.828770759094287e-12, 6.456457160755703e-12])
See also
Ramp-Response Plot
- control_plots.ramp_response_plot(slope=1, color='b', prec=8, lower_limit=0, upper_limit=10, show_axes=False, grid=True, show=True, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the ramp response of a continuous-time system.
Ramp function is defined as the straight line passing through origin (\(f(x) = mx\)). The slope of the ramp function can be varied by the user and the default value is 1.
- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant type
The LTI SISO system for which the Ramp Response is to be computed.
slope : Number, optional
The slope of the input ramp function. Defaults to 1.
color : str, tuple, optional
The color of the line. Default is Blue.
show : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will be displayed otherwise the equivalent matplotlibplotobject will be returned. Defaults to True.lower_limit : Number, optional
The lower limit of the plot range. Defaults to 0.
upper_limit : Number, optional
The upper limit of the plot range. Defaults to 10.
prec : int, optional
The decimal point precision for the point coordinate values. Defaults to 8.
show_axes : boolean, optional
If
True, the coordinate axes will be shown. Defaults to False.grid : boolean, optional
If
True, the plot will have a grid. Defaults to True.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import ramp_response_plot >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s, (s+4)*(s+8), s) >>> ramp_response_plot(tf1, upper_limit=2)
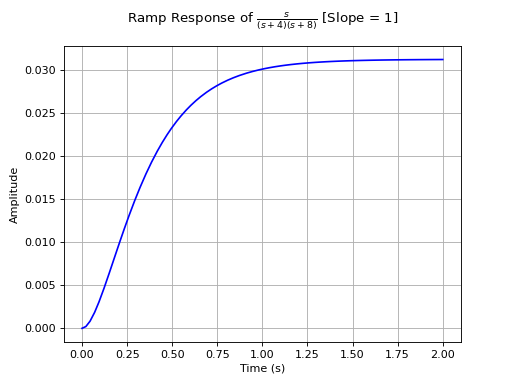
See also
References
- control_plots.ramp_response_numerical_data(slope=1, prec=8, lower_limit=0, upper_limit=10, **kwargs)[source]
Returns the numerical values of the points in the ramp response plot of a SISO continuous-time system. By default, adaptive sampling is used. If the user wants to instead get an uniformly sampled response, then
adaptivekwarg should be passedFalseandnb_of_pointsmust be passed as additional kwargs. Refer to the parameters of classsympy.plotting.plot.LineOver1DRangeSeriesfor more details.- Parameters
system : SISOLinearTimeInvariant
The system for which the ramp response data is to be computed.
slope : Number, optional
The slope of the input ramp function. Defaults to 1.
prec : int, optional
The decimal point precision for the point coordinate values. Defaults to 8.
lower_limit : Number, optional
The lower limit of the plot range. Defaults to 0.
upper_limit : Number, optional
The upper limit of the plot range. Defaults to 10.
kwargs :
Additional keyword arguments are passed to the underlying
sympy.plotting.plot.LineOver1DRangeSeriesclass.- Returns
tuple : (x, y)
x = Time-axis values of the points in the ramp response plot. NumPy array. y = Amplitude-axis values of the points in the ramp response plot. NumPy array.
- Raises
NotImplementedError
When a SISO LTI system is not passed.
When time delay terms are present in the system.
ValueError
When more than one free symbol is present in the system. The only variable in the transfer function should be the variable of the Laplace transform.
When
lower_limitparameter is less than 0.When
slopeis negative.
Examples
>>> from sympy.abc import s >>> from sympy.physics.control.lti import TransferFunction >>> from sympy.physics.control.control_plots import ramp_response_numerical_data >>> tf1 = TransferFunction(s, s**2 + 5*s + 8, s) >>> ramp_response_numerical_data(tf1) (([0.0, 0.12166980856813935,..., 9.861246379582118, 10.0], [1.4504508011325967e-09, 0.006046440489058766,..., 0.12499999999568202, 0.12499999999661349]))
See also